


 Français
Français
Understanding > Fundamental concepts > Phenomena X
Oppositions, conjunctions, quadratures, elongations
access to the tables of dates of oppositions and elongations
These words correspond to specific configurations of celestial bodies, selected because they allow an easy observation of a planet or because they mean that no observation is possible.
Definitions :
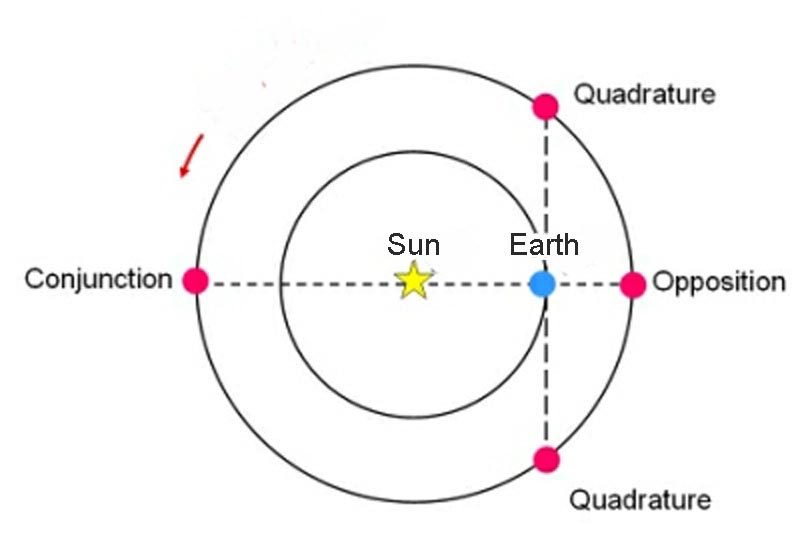
Opposition:
Opposition of a planet with another celestial body: phenomenon for which the celestial geocentric
longitudes of the planet and of the other body differ from 180° .
An opposition may concern two planets but it is mainly the opposition of a planet and the Sun
which is looked for because such configuration corresponds to favorable conditions
for the observation of the planet.
Opposition of a planet with the Sun:
this configuration concerns only the
Conjunction:
Conjunction between a planet and one or several celestial bodies:
phenomenon corresponding to the time when two or more celestial bodies
have the same celestial geocentric longitudes, that means that
these bodies are very close in the sky.
Conjunction of a superior planet with the Sun : the celestial geocentric longitudes
(or right ascensions) of the planet and the Sun are equal.
Conjunction of Mercury or Venus with the Sun : the celestial geocentric longitudes
(or right ascensions) of the planet and the Sun are equal,
the conjunction is superior or inferior depending that the Sun is
between the Earth and the planet or that the planet is between the Earth and the Sun.
Conjunction of two planets, of a planet with the Moon or with a star:
the right ascensions of the two bodies are considered to be equal.
The conjunction between a planet and the Moon is often spectacular
when the Moon occults the planet.
Quadrature:
Configuration concerning the superior planets only:
Quadrature of a planet superior with the Sun: configuration for which the celestial geocentric
longitudes of the planet and the Sun differ from 90°.
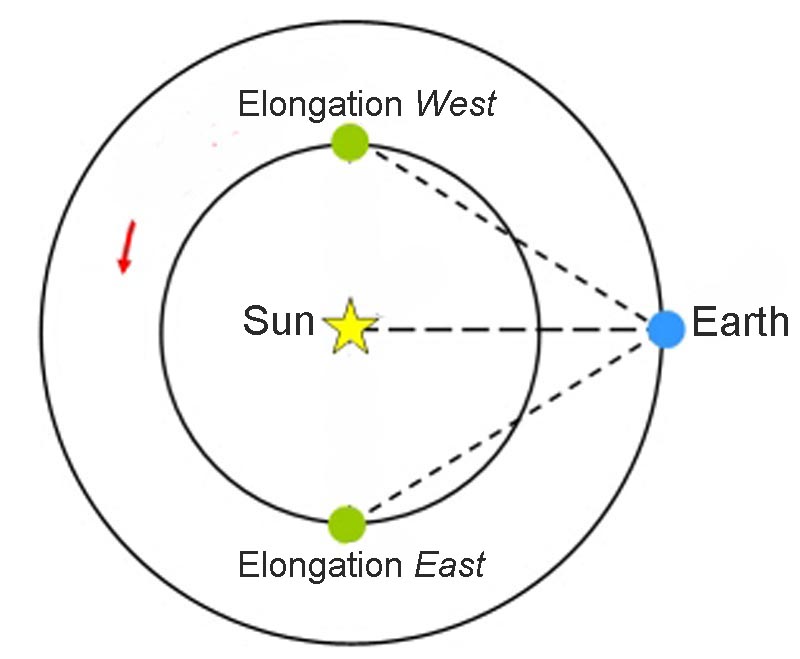
Elongation:
Configuration concerning the inferior planets only:
Maximum elongation: it is the configuration for which the angular apparent distance
between the planet and the Sun is the largest. The inferior planets
may never be in opposition with the Sun and the maximum elongation is
the configuration allowing the best condition for observing the planet.
When Mercury and Venus are close to their largest "East" elongation, they are
visible after Sunset. Similarly, when they are close to their largest
"West" elongation, they are visible before Sunrise.
For the superior planets of the Solar System, the maximum elongation
corresponds to an opposition, i.e. to an elongation of 180°.
Duration between two oppositions (example of Mars):
The mean angular velocity (sidereal) of the Earth is n1 = 6.28307585 radians/year and the one
of Mars n2 = 3.34061243 radians/year. If we start at a given opposition, the next one will occur
when the Earth gains one revolution to Mars, i.e.
n1*t = n2*t + 2 pi
so that, after (in years)
t1 = 2 pi/(n1-n2)
i.e., in number of revolution for the Earth (or number of years)
nopp = t1/T1=n1/(n1-n2) = 2.135311456 revolutions or years
So it is necessary to wait 2 years and 49 days to have a new opposition.
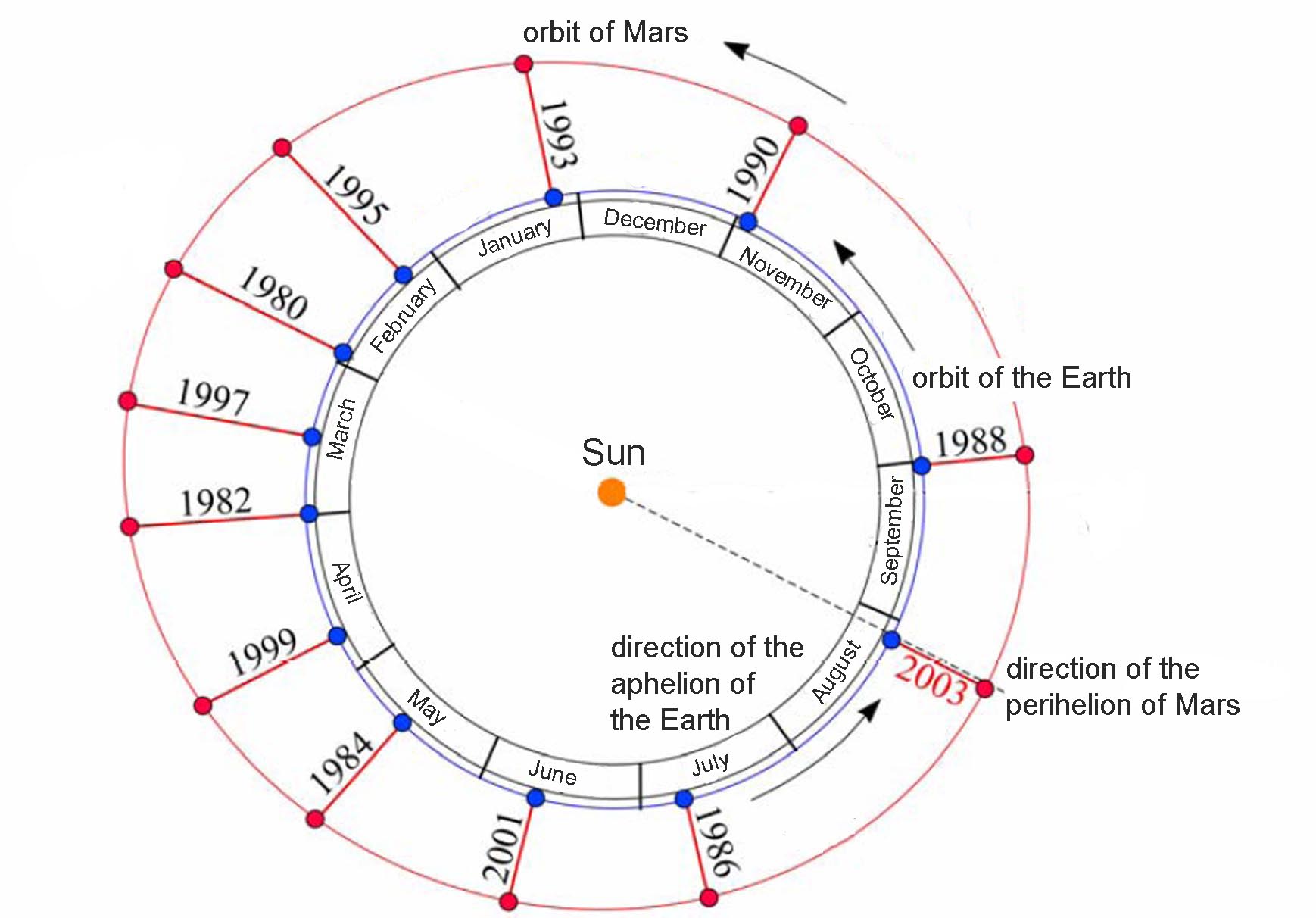
are the most favorable. Note that the aphelion of the Earth is not far that make such opposition more favorable.
Specific case of Mars:
the planet Mars has its closest approach of the Earth at the time of
the opposition but this
distance varies for each opposition because of the ellipticity of the orbits
of the Earth and Mars. This minimum distance at opposition may vary from
one to two and, some oppositions
are much more favorable to the observation of Mars.
The oppositions of Mars at the present time are as follows:
| Dates | Distance to the Earth in AU |
Apparent diameter in arcsec |
|---|---|---|
| 13 June 2001 | 0.4556 | 21" |
| 28 August 2003 | 0.3728 | 25" |
| 7 November 2005 | 0.4700 | 21" |
| 24 December 2007 | 0.5929 | 17" |
| 29 January 2010 | 0.6644 | 14" |
| 3 March 2012 | 0.6741 | 14" |
| 8 April 2014 | 0.6209 | 15" |
| 22 May 2016 | 0.5094 | 19" |
| 27 July 2018 | 0.3862 | 24" |
| 13 October 2020 | 0.4192 | 23" |
| 8 December 2022 | 0.5496 | 18" |
| 16 January 2025 | 0.6437 | 15" |
| 19 February 2027 | 0.6779 | 14" |
| 25 March 2029 | 0.6491 | 15" |
The moire favorable oppositions of Mars:
date distance Earth-Mars apparent diameter
(au) (millions of km) of Mars
25 August 1719 0.374010 55.951 25.05"
13 August 1766 0.373260 55.839 25.10"
18 August 1845 0.373021 55.803 25.11"
22 August 1924 0.372846 55.777 25.12"
27 August 2003 0.372719 55.758 25.13"
15 August 2050 0.374051 55.957 25.04"
30 August 2082 0.373564 55.884 25.08"
19 August 2129 0.373276 55.841 25.10"
24 August 2208 0.372794 55.769 25.13"
28 August 2287 0.372254 55.688 25.16"
access to the tables of dates of oppositions and elongations
Credit : J.E. Arlot, IMCCE/observatoire de Paris



