
- Encyclopedia
- Discovery
- Space
- Observatories
- Understanding


 Français
Français
Understanding > Fundamental concepts
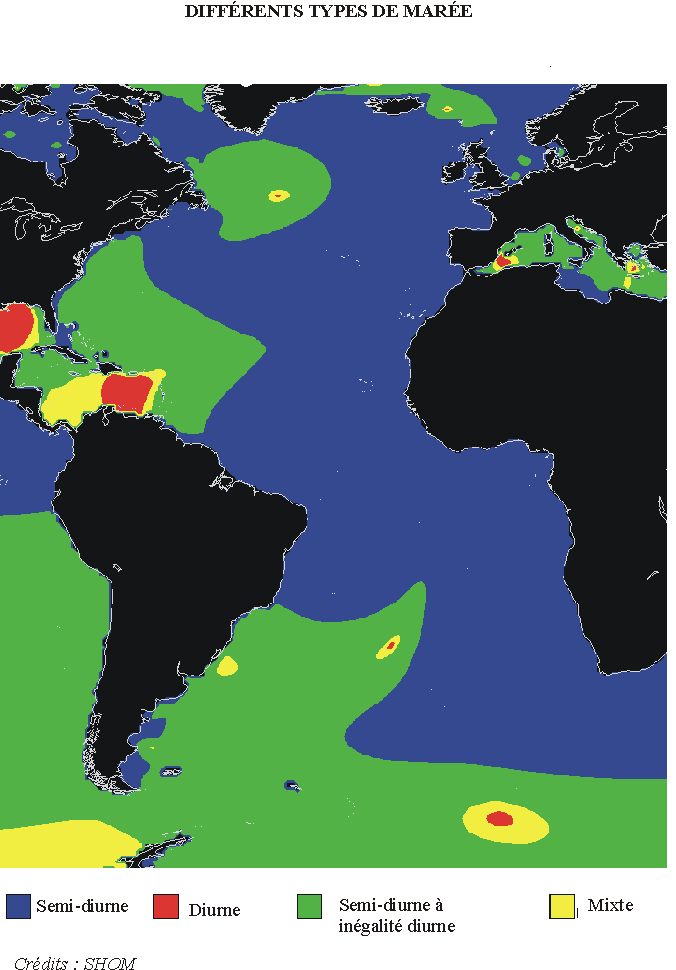
Maps of tides
Maps showing the different zones where are semi-diurnal tides, semi-diurnal tides with diurnal inegalities, mixte tides and diurnal tides :
Atlantic ocean and Mediterranean sea :
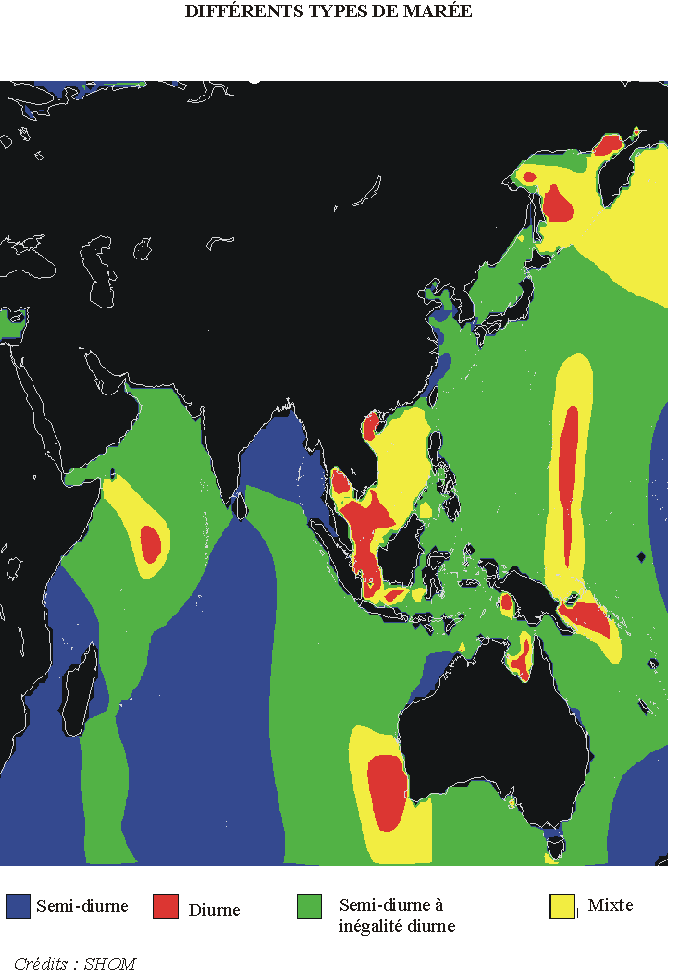
Indian ocean and Oceania :
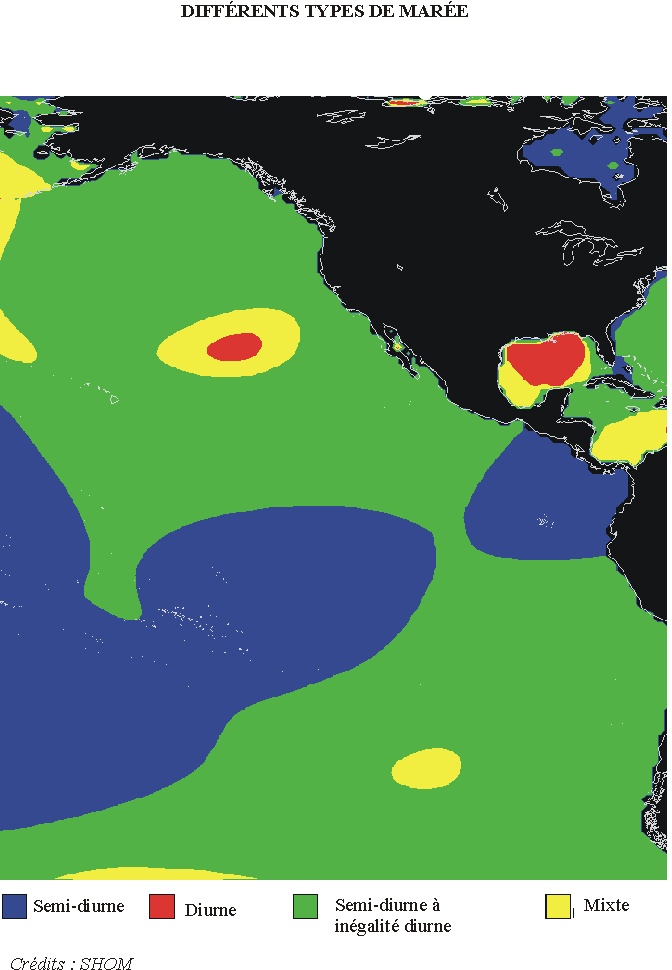
Pacific ocean :
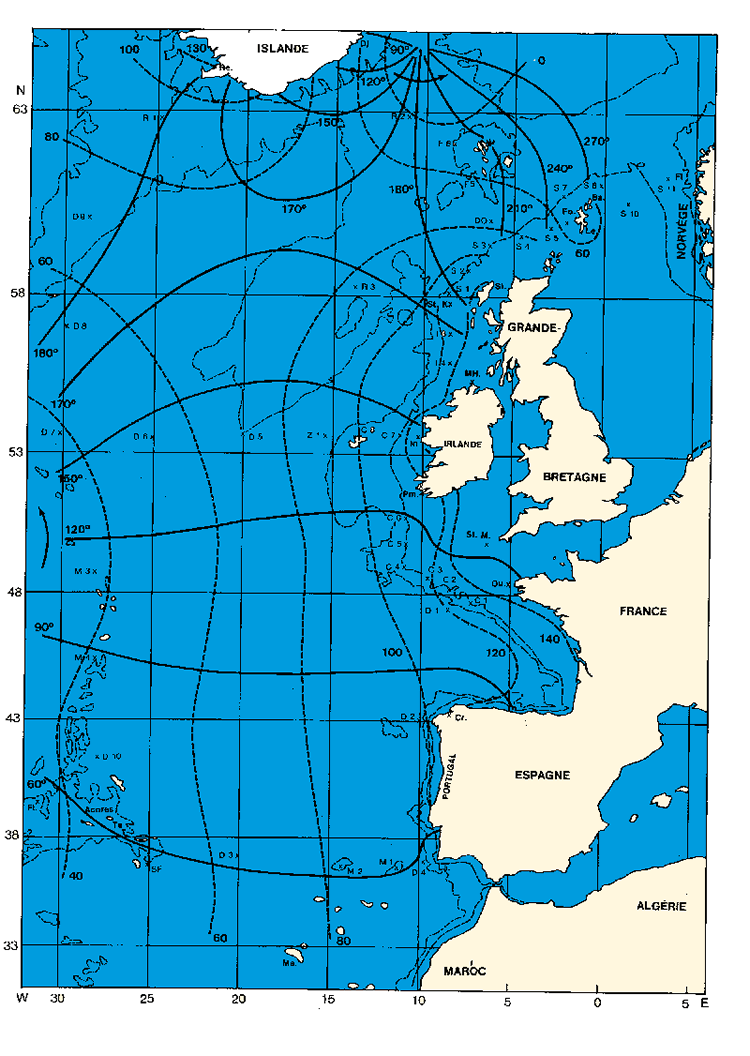
Evolution of the tide in the North Atlantic ocean in the vicinity of the French coasts.
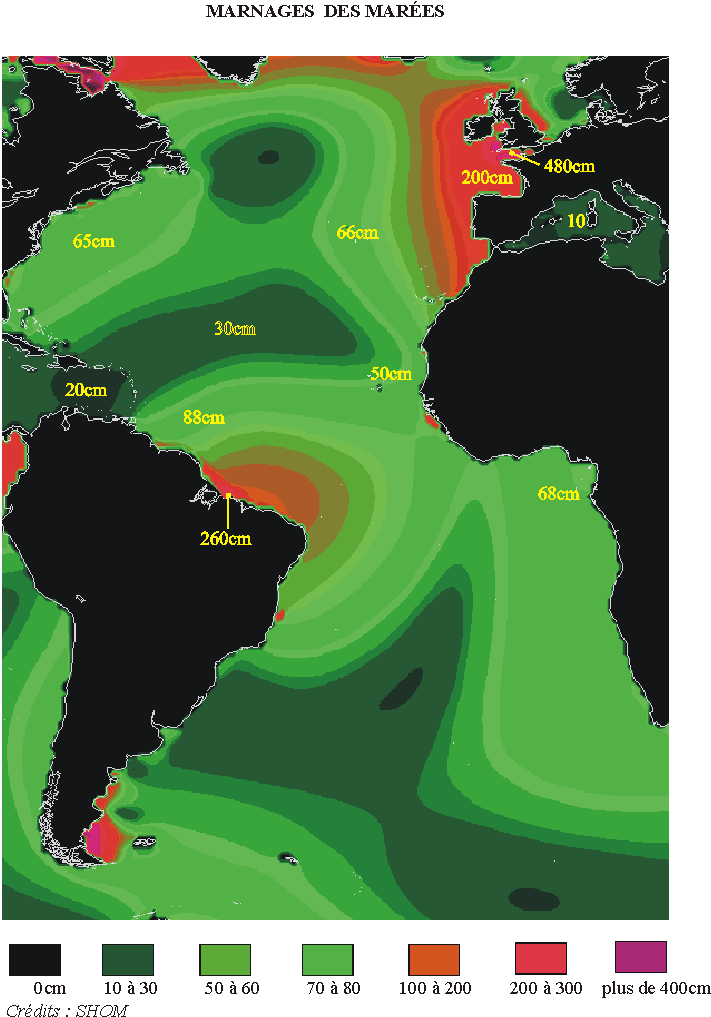
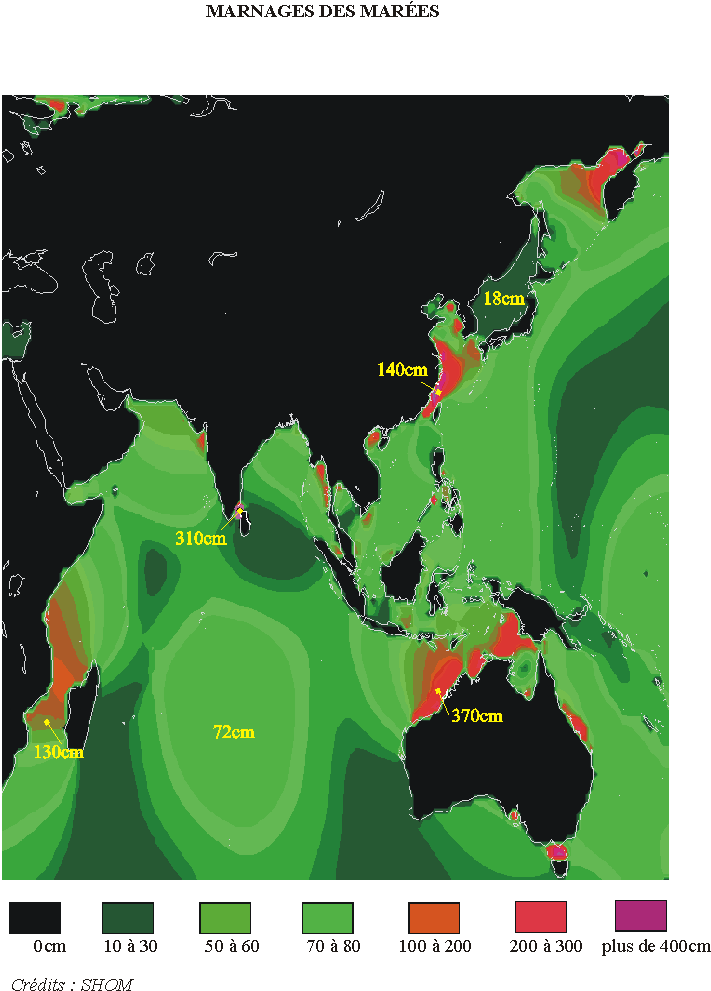
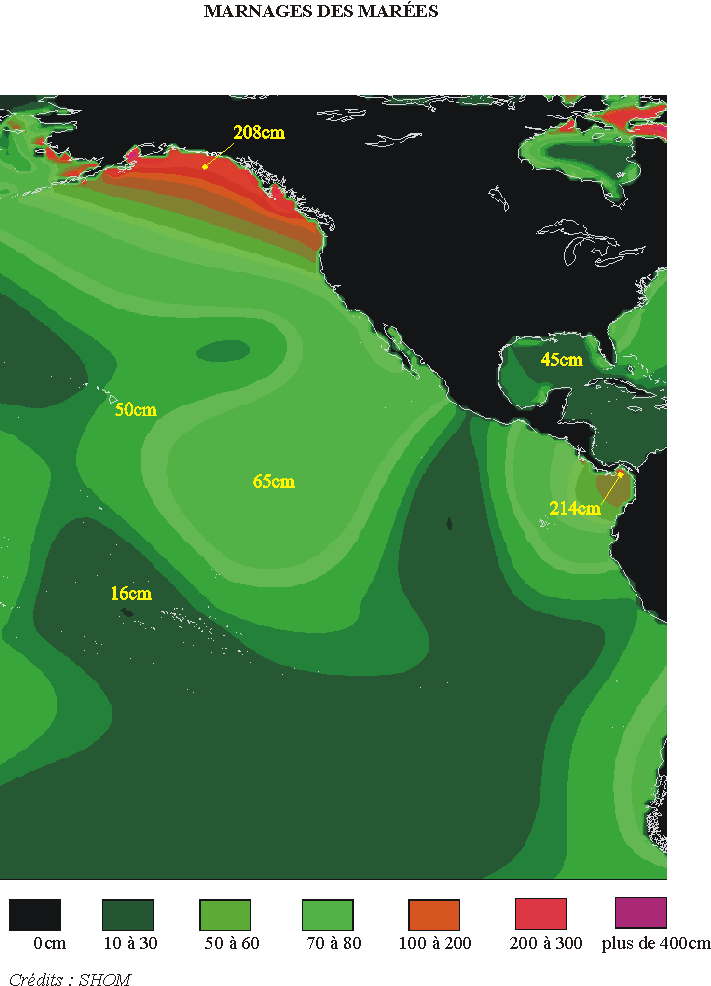
Mean drowdown observed worldwide
Atlantic ocean and Mediterranean sea :
Indian ocean and Oceania :
Pacific ocean :
Credit : P. RocherIMCCE



